Fumbling in the dark
The Cass review holds up a snapshot of missing data, cluelessness and fudging of evidence in gender medicine around the world

Nine of the 15 gender clinics in a landmark international survey for the Cass review have admitted they do not routinely collect outcome data on their young patients.
This survey, together with a new evaluation of treatment guidelines for gender dysphoria, gives unprecedented insights into the workings of gender clinics around the world offering puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones to minors.
In the 2022-23 survey, six clinics said they “routinely collected some outcome data”: one of these clinics gave no further detail; one noted the number of patients discontinuing treatment; another used measures of quality of life; two were taking part in cohort studies; and the sixth clinic repeated some baseline assessments. Nine clinics acknowledged “not routinely collecting outcome data.”
The report of the survey results1, published by researchers from the University of York earlier this month, identified clinics by country, not name. Of the clinics that took part, Australia and the Netherlands were prominent with five and four clinics respectively.
Poor data collection was central to the controversy over the London-based Tavistock youth gender clinic.
The Cass review had planned to run a data-linkage study—with help from adult gender clinics—to learn the outcomes of the Tavistock’s 9,000-odd former patients.
The missing long-term data would allow clinicians, young patients and parents to make informed decisions about treatment. The review said it was to be the largest study of its kind in the world.
However, six of the seven adult clinics refused to co-operate. One stated reason was that “the study outcomes focus on adverse health events, for which the clinics do not feel primarily responsible.”
Another adult clinic said, “The unintended outcome of the study is likely to be a high-profile national report that will be misinterpreted, misrepresented or actively used to harm patients and disrupt the work of practitioners across the gender dysphoria pathway.”
On April 12, however, The Times newspaper reported that the uncooperative adult clinics had “bowed to pressure to share [the] missing data”.
Mostly medical
In the York University international survey, ordered by the Cass review, all 15 youth gender clinics said they used a multi-disciplinary team, but researchers concluded there was a “paucity” of psychosocial therapy interventions such as psychotherapy or cognitive behaviour therapy. Five clinics did not offer any of these non-medical interventions in-house.
All gender clinics told researchers that “genital reconstructive surgery”—the creation of a pseudo vagina, for example—was “accessible only from age 18.” The youngest age for “masculinising chest surgery” (a double mastectomy) was reported as 16. In fact, there are documented cases in Australia of 15-year-olds approved for transgender mastectomy. Genital surgery is legally available to minors2 in Australia and practised in America.
“Only five clinics reported routine discussion of fertility3 preferences, and only two discussed sexuality4. Finland was the only country to report routinely assessing for history of trauma5,” the final Cass report says in its commentary on the survey.
In separate studies for the Cass review, three independent reviewers evaluated the quality of 21 guidelines for treatment of gender dysphoria in minors.
Included were international guidelines (from the Endocrine Society and the World Professional Association for Transgender Health or WPATH); documents from North America (for example, the 2018 policy statement from the American Academy of Pediatrics); from Europe (the guideline of the UK Royal College of Psychiatrists, for example, and Denmark’s); as well as guidelines from the Asia-Pacific and Africa.
“WPATH has been highly influential in directing international practice, although its guidelines were found by the University of York appraisal process to lack developmental rigour,” the Cass report says.
The York researchers chart patterns of “circular” cross-referencing between guidelines to create a misleading impression of consensus in favour of the medicalised “gender-affirming” treatment approach.
“The guideline appraisal raises serious questions about the reliability of current guidelines. Most guidelines have not followed the international standards for [rigorous and independent] guideline development. Few guidelines are informed by a systematic review of empirical evidence [the gold standard for assessing the evidence supporting a health intervention] and there is a lack of transparency about how recommendations were developed,” the Cass report says.
“Healthcare services and professionals should take into account the variable quality of published guidelines to support the management of children and young people experiencing gender dysphoria. The lack of independence in many national and regional guidelines, and the limited evidence-based underpinning current guidelines, should be considered when utilising these for practice.”
The Cass report says it is “imperative” that gender clinic staff be “cognisant of the limitations in relation to the evidence base and fully understand the knowns and the unknowns.”
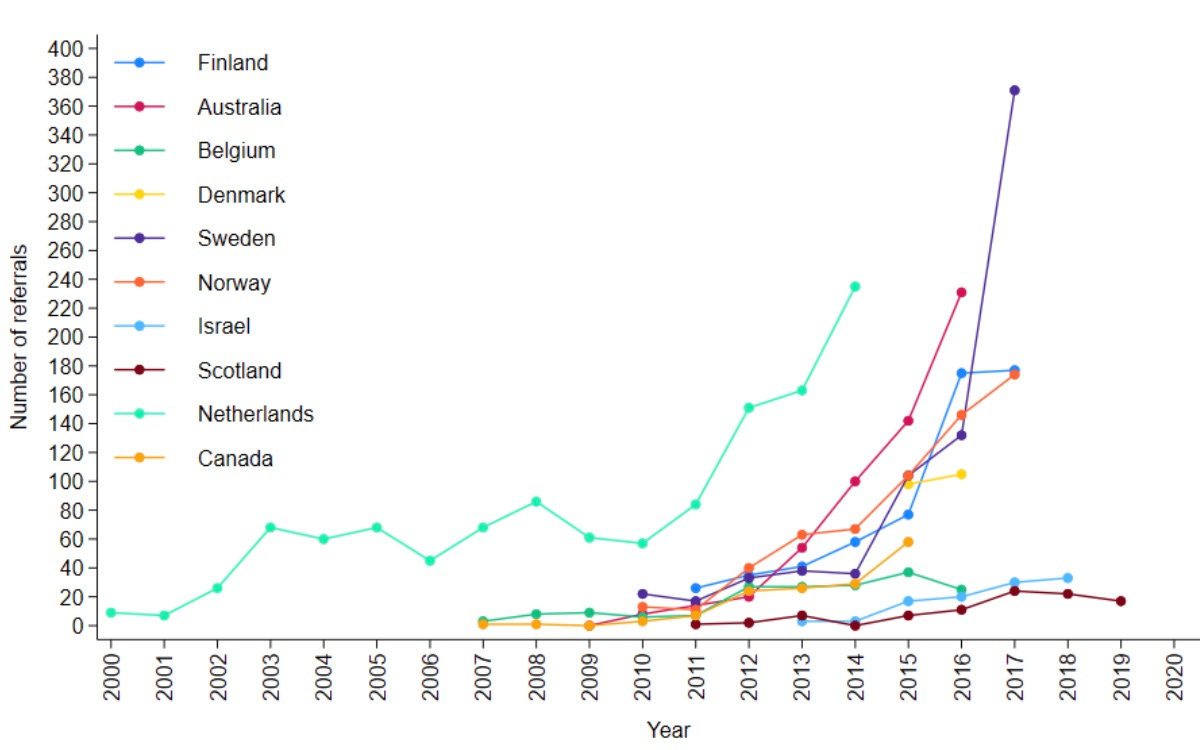
Chart: Number of youth gender clinic referrals over time by country. Source: Cass report
Bum steer
Staff at the Tavistock clinic misled patients and parents, or failed to correct their misconceptions, according to a new report from the Multi-Professional Review Group (MPRG) given oversight of treatment decisions from 2021.
These shortcomings of clinicians included playing down the extent of the unknowns of hormonal treatment; not explaining that puberty blockers are being used unlicensed and off-label; not challenging the reassuring but false parallel with the licensed use of puberty blockers for precocious (premature) puberty; not discussing the possibility that blockers will pause or slow psychosexual development; and not sharing figures showing the vast majority of children started on puberty blockers will go on to cross-sex hormones supposed to be taken lifelong.
The MPRG was also troubled by clinical documents showing misunderstanding of “the outcome of physical treatments” on the part of patients and parents.
In the York University study of treatment guidelines for gender dysphoria, only two were recommended for use by all three reviewers. These were recent, more cautious policies from Finland and Sweden. Both followed independent systematic reviews showing the evidence base for hormonal and surgical treatment of minors to be very weak and uncertain. Like the Cass review itself, the 2020 Finnish and 2022 Swedish guidelines recognise that puberty blockers are experimental and should not be routine treatment.
Although all the guidelines in the study agreed on the need for a multidisciplinary team to treat gender-distressed minors, the “most striking problem” shown by analysis of these documents was “the lack of any consensus6 on the purpose of the assessment process”, the Cass report says.
“Some guidelines were focused on diagnosis, some on… eligibility for hormones, some on psychosocial assessment, and some on readiness for medical interventions7.
“Only the Swedish and [the 2022] WPATH 8th version guidelines contain detail on the assessment process8. Both recommend that the duration, structure and content of the assessment be varied according to age, complexity and gender development.
“Very few guidelines recommend formal measures/clinical tools to assess gender dysphoria, and a separate analysis demonstrated that the formal measures that exist are poorly validated.”
Nor was there any consensus on “when psychological or hormonal interventions should be offered and on what basis.”
A survey of staff at the Tavistock clinic, undertaken as part of the Cass review, found specialists divided on whether or not “assessment should seek to make a differential diagnosis, ruling out other potential [non-gender9] causes of the child or young person’s distress.”
Arguing for an ambitious research program well beyond a possible clinical trial of puberty blockers, the Cass report says the field of youth gender dysphoria is one of “remarkably weak evidence” where health professionals are “afraid to openly discuss their views” because of vilification and bullying.
“Although some think the clinical approach should be based on a social justice model, the NHS works in an evidence-based way,” the report says.
“The gaps in the evidence base regarding all aspects of gender care for children and young people have been highlighted, from epidemiology through to assessment, diagnosis10 and intervention. It is troubling that so little is known about this cohort and their outcomes.
“Based on a single Dutch study, which suggested that puberty blockers may improve psychological wellbeing for a narrowly defined group of children with gender incongruence [or dysphoria], the practice spread at pace to other countries.
“Some practitioners abandoned normal clinical approaches to holistic assessment, which has meant that this group of [gender-distressed] young people have been exceptionalised compared to other young people with similarly complex presentations.”
Chart: Age and sex on referral to the Tavistock clinic from 2018-2022. Source: Cass report
Who to trust?
The Cass report says the missing evidence “makes it difficult to provide adequate information on which a young person and their family can make an informed choice.”
“A trusted source of information is needed on all aspects of medical care, but in particular it is important to defuse/manage expectations that have been built up by claims about the efficacy of puberty blockers.
“The option to provide masculinising or feminising hormones from the age of 16 is available, but the [Cass] review would recommend an extremely cautious clinical approach and a strong clinical rationale for providing hormones before the age of 18. This would keep options open during this important developmental window, allowing time for management of any co-occurring [non-gender] conditions11, building of resilience, and fertility preservation, if required.”
The review stresses that “consent is more than just capacity and competence. It requires clinicians to ensure that the proposed intervention is clinically indicated as they have a duty to offer appropriate treatment. It also requires the patient to be provided with appropriate and sufficient information about the risks, benefits and expected outcomes of the treatment.”
“Assessing whether a hormone pathway is indicated is challenging. A formal diagnosis of gender dysphoria is frequently cited as a prerequisite for accessing hormone treatment. However, it is not reliably predictive of whether that young person will have long-standing gender incongruence in the future, or whether medical intervention will be the best option for them.”
Advocates for the gender-affirming approach assert that detransition and treatment regret are vanishingly rare, whereas suicide risk for those denied medical intervention is claimed to be very high.
The Cass report says: “It has been suggested that hormone treatment reduces the elevated risk of death by suicide in this population, but the evidence found did not support this conclusion.”
“The percentage of people treated with hormones who subsequently detransition remains unknown due to the lack of long-term follow-up studies, although there is suggestion that numbers are increasing.”
The report cites three reasons why the true extent of detransition is unlikely to be clear for some time—patients who decide medicalisation was a mistake may not wish to return to their former clinic to announce this fact; there is a post-treatment honeymoon period and clinicians suggest it may take 5-10 years before a decision to detransition; and the surge in patient numbers only began within the last decade.
Faced with uncertainty and a lack of good evidence, those with responsibility—from health ministers and hospital managers down to gender clinicians—rely on treatment guidelines supposed to advise on clinical practice according to the “best-available” evidence and expert opinion.
In the York University guideline analysis, the 21 documents were rated on six domains, the key two being the rigour of their development and their editorial independence.
“[Rigour] includes systematically searching the evidence, being clear about the link between recommendations and supporting evidence, and ensuring that health benefits, side effects and risks have been considered in formulating the recommendations,” the Cass report says.
Only the Finnish and Swedish guidelines scored above 50 per cent for rigour. Only these two documents, the Cass report says, link “the lack of robust evidence about medical treatments to a recommendation that treatments should be provided under a research framework or within a research clinic. They are also the only guidelines that have been informed by an ethical review conducted as part of the guideline development.”
“Most of the guidelines described insufficient evidence about the risks and benefits of medical treatment in adolescents, particularly in relation to long-term outcomes. Despite this, many then went on to cite this same evidence to recommend medical treatments,” the report says.
“Alternatively, they referred to other guidelines that recommend medical treatments as their basis for making the same recommendations. Early versions of two international guidelines, the Endocrine Society 2009 and WPATH 7th version guidelines, influenced nearly all the other guidelines.
“These two guidelines are also closely interlinked, with WPATH adopting Endocrine Society recommendations, and acting as a co-sponsor and providing input to drafts of the Endocrine Society guideline. The WPATH 8th version cited many of the other national and regional guidelines to support some of its recommendations, despite these guidelines having been considerably influenced by the WPATH 7th version.
“The circularity of this approach may explain why there has been an apparent consensus on key areas of practice despite the evidence being poor.”
Sometimes these gender-affirming guidelines seek to buttress a strong evidence claim with a citation to a study that is weak or involves a different patient group.
The Cass report notes that, “The WPATH 8th version’s narrative on gender-affirming medical treatment for adolescents does not reference its own systematic review [of the evidence], but instead states: ‘Despite the slowly growing body of evidence supporting the effectiveness of early medical intervention, the number of studies is still low, and there are few outcome studies that follow youth into adulthood. Therefore, a systematic review regarding outcomes of treatment in adolescents is not possible’.”
Despite WPATH insisting such an evidence review is not possible, this is precisely what health authorities and experts have undertaken since 2019 in several jurisdictions—Finland, Sweden, the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, Florida, Germany, and University of York research commissioned by the Cass review.
Yet in the 8th and current version of its guideline, WPATH makes the confident statement that, “There is strong evidence demonstrating the benefits in quality of life and well-being of gender-affirming treatments, including endocrine and surgical procedures… Gender-affirming interventions are based on decades of clinical experience and research; therefore, they are not considered experimental, cosmetic, or for the mere convenience of a patient. They are safe and effective at reducing gender incongruence and gender dysphoria”.
But WPATH “overstates the strength of the evidence” for its treatment recommendations, the Cass report says.
In the survey, there was one clinic each from Belgium, Denmark, Finland, Northern Ireland, Norway and Spain. The response rate was 38 per cent.
In Australia there is no good public data on trans surgery for minors.
Early puberty blockers followed by cross-sex hormones are expected to sterilise young people and may also impair future sexual function.
Some sizeable proportion of gender clinic patients might grow up in healthy bodies and accept their same-sex attraction were it not for trans medicalisation, according to testimony from detransitioners, clinicians’ reports and data.
Trauma from a history of sexual abuse, for example, or exposure to domestic violence is thought to be among the many possible underlying causes of what presents as gender dysphoria. The Multi-Professional Review Group (MPRG), given oversight of Tavistock treatment decisions from 2021-23, was troubled by the lack of curiosity by the clinic’s staff about the effect of a child’s “physical or mental illness within the family, abusive or addictive environments, bereavement, cultural or religious background, etc.”
Critics of the “gender-affirming” treatment approach say it is not mainstream medicine because the “trans child” in effect self-diagnoses while clinicians avoid differential diagnosis and attribute mental health disorders and other pre-existing issues to a “transphobic” society.
“In most cases [at the Tavistock clinic] children and parents were asking to progress on to puberty blockers from the very first appointment”, according to the MPRG.
In the MPRG’s opinion, the patient notes from the Tavistock “rarely provide a structured history or physical assessment, however the submissions to the MPRG suggest that the children have a wide range of childhood, familial and congenital conditions.”
Once referred to the Tavistock, patients typically were no longer seen by child and adolescent mental health services.
According to the MPRG, gender dysphoria in the diagnostic manual DSM-5 “has a low threshold based on overlapping criteria, and is likely to create false positives. Young people who do not go on to have an enduring cross-sex gender identity may have met the criteria in childhood. And early to mid-childhood social transition may be influential in maintaining adherence to the criteria. Sex role and gender expression stereotyping is present within the diagnostic criteria—preferred toys, clothes, etc—not reflecting that many toys, games and activities [today] are less exclusively gendered than in previous decades.”
The MPRG said it was “notable that until the child and family’s first appointment at [the Tavistock] they have received little, if any, support from health, social care, or education professionals. Most children and parents have felt isolated and desperate for support and have therefore turned for information to the media and online resources, with many accessing LGBTQ+ and [gender dysphoria] support groups or private providers which appear to be mainly ‘affirmative’ in nature, and children and families have moved forward with social transition. This history/journey is rarely examined closely by [Tavistock clinicians] for signs of difficulty [or] regret.”



I believe that the Cass report goes a long way to condemning the ‘affirmative model of gender care’.
I suspect that formal investigations will soon be proposed, Royal Commission type formal investigations.
It is probable that the party is all but over.
However, where would that leave those practitioners who have promoted and implemented this ‘cure’, a cure that required the use of off-label hormones and all the horrors that followed?
Those practitioners would become very vulnerable. God-knows the damage done cannot be reversed, reputations and careers at stake. The lawyers will be licking their chops.
It is difficult to imagine a scenario where a “whoops, sorry” would suffice.
"The WPATH 8th version’s narrative on gender-affirming medical treatment for adolescents does not reference its own systematic review [of the evidence], but instead states: ‘... a systematic review regarding outcomes of treatment in adolescents is not possible.'"
That really sums up gender affirming medicine. Constantly rewriting history. We're seeing that in the reactions to the CASS report as well.